Basic Concepts¶
At the most fundamental level, Fancy Zones works by:
- Adding metadata to application windows indicating their size, origin, and "zone"
- Listening for window events (drag, resize) and "hooking" them
Window Properties¶
Metadata can be added to windows by leveraging Window Properties:
A window property is any data assigned to a window. A window property is usually a handle of the window-specific data, but it may be any value. Each window property is identified by a string name.
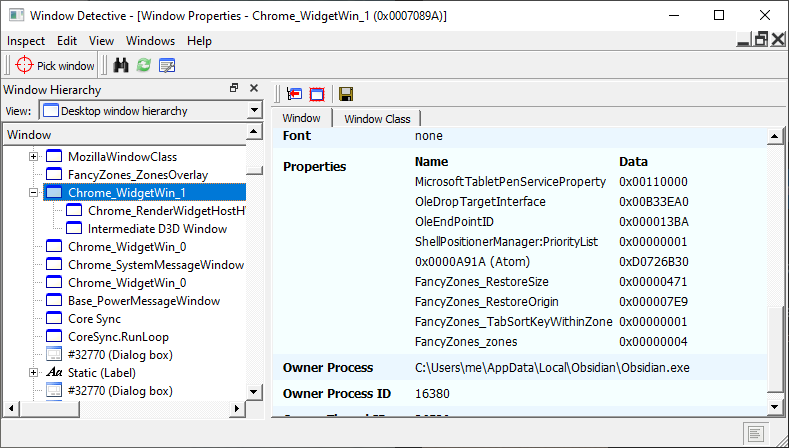
Window Detective can be used to view Window Properties. In the example below, the picked window has the following Fancy Zones properties: - FancyZones_RestoreSize - FancyZones_RestoreOrigin - FancyZones_TabSortKeyWithinZone - FancyZones_zones
FancyZonesWindowProperties¶
FancyZonesWindowProperties.hcontains defines for all window properties used by Fancy Zones.- FancyZonesWindowProperties.cpp contains the
StampZoneIndexProperty()method, used to "stamp" window properties to window handles.
Windows Events¶
Windows is an event-based operating system, meaning, all windows generate and consume events. Events can broadly be divided into two types:
- WinEvents - Messages
WinEvents¶
Microsoft defines WinEvents thusly:
Server applications and the operating system use WinEvents to notify clients when a change occurs in the system or in the user interface.
WinEvent support is a feature of the Windows operating system that provides:
- A simple way for clients to register for event notifications.
- A mechanism for injecting client code into servers.
- Routing of events from servers to interested clients.
- Automatic event generation for most HWND-based controls.
An application can "listen" for events by registering a hook.
Windows Hooks¶
Microsoft defines hooks thusly:
A hook is a mechanism by which an application can intercept events, such as messages, mouse actions, and keystrokes. A function that intercepts a particular type of event is known as a hook procedure. A hook procedure can act on each event it receives, and then modify or discard the event.
Hooks can be one of the following: - In-Context - Out-of-Context
There are two types of hooks thread and global. Global hooks require DLL-injection.
Hooks are set by registering a WinEventProc callback function using SetWinEventHook.
FancyZonesApp.cpp¶
Fancy Zones calls SetWinEventHook in FancyZonesApp::InitHooks() to subscribe to the following system-level and object-level events.
std::array<DWORD, 7> events_to_subscribe = {
EVENT_SYSTEM_MOVESIZESTART,
EVENT_SYSTEM_MOVESIZEEND,
EVENT_OBJECT_NAMECHANGE,
EVENT_OBJECT_UNCLOAKED,
EVENT_OBJECT_SHOW,
EVENT_OBJECT_CREATE,
EVENT_OBJECT_LOCATIONCHANGE
};
These event constants are detailed in the Windows documentation here, Event Constants.
The hooked events are received in FancyZonesApp and ultimately translated into Windows Messages which are consumed by the Fancy Zones message loop defined inFancyZones.cpp.
FancyZones.cpp¶
The FancyZones class is where most of the Fancy Zones business logic is defined.
FancyZones::HandleWinHookEvent() translates received events into internal Windows Messages which are consumed in FancyZones::WndProc().
Windows Messages¶
Windows Messages are a type of event used by the operating system to provide external input to a window:
Unlike MS-DOS-based applications, Windows-based applications are event-driven. They do not make explicit function calls (such as C run-time library calls) to obtain input. Instead, they wait for the system to pass input to them.
The system passes all input for an application to the various windows in the application. Each window has a function, called a window procedure, that the system calls whenever it has input for the window. The window procedure processes the input and returns control to the system. For more information about window procedures, see Window Procedures.
At the most basic level, all Windows GUI applications are simply a window and a message loop.
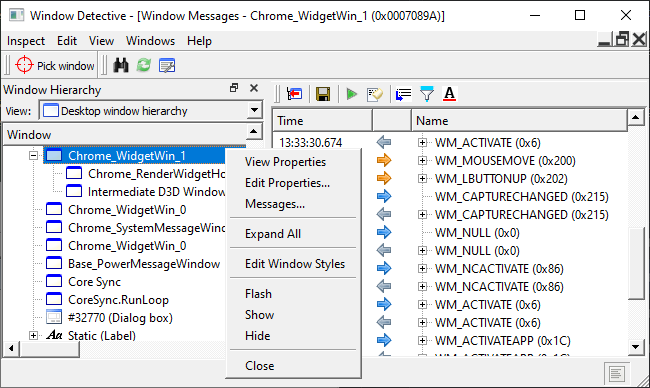
Windows Detective can be used to view Windows Events by right-clicking on a window handle and selecting "Messages".
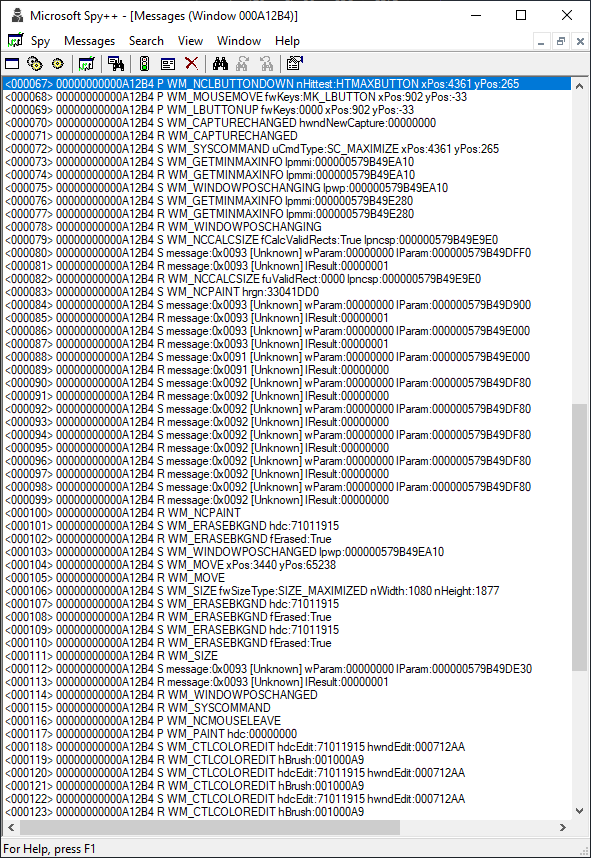
Clicking Maximize button on Notepad Toolbar¶
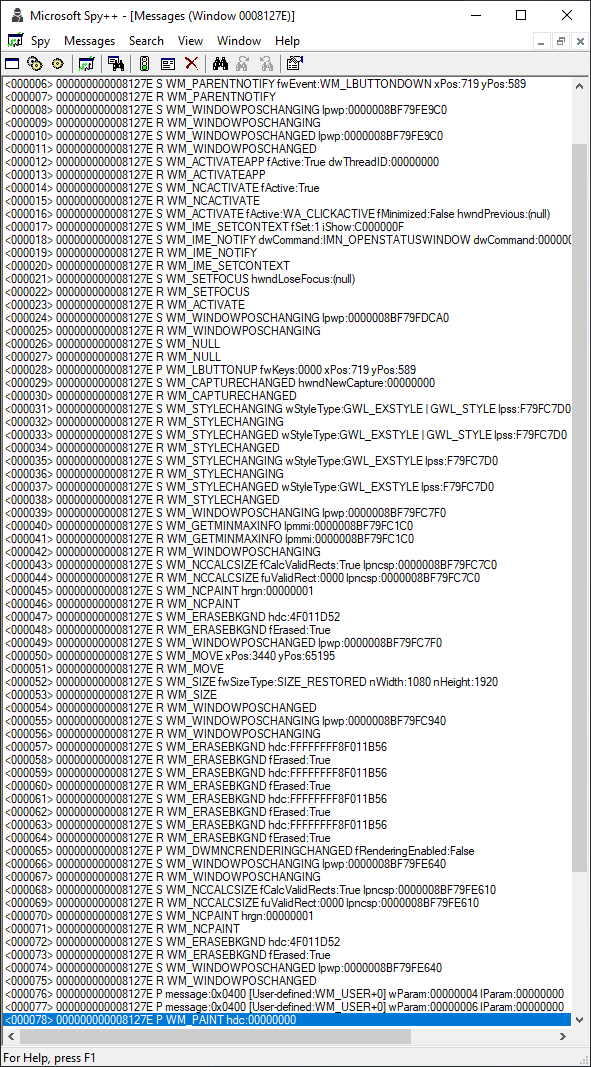
Clicking "Full Screen" Button in Youtube on Chrome¶
"Maximize in Zone" Implementation¶
Example 1: Basic Implementation¶
Implementing a feature which resizes a "maximized" window so that it fits within the zone it is currently in.
First, we need to determine what event is generated when the "maximize" button is pressed.
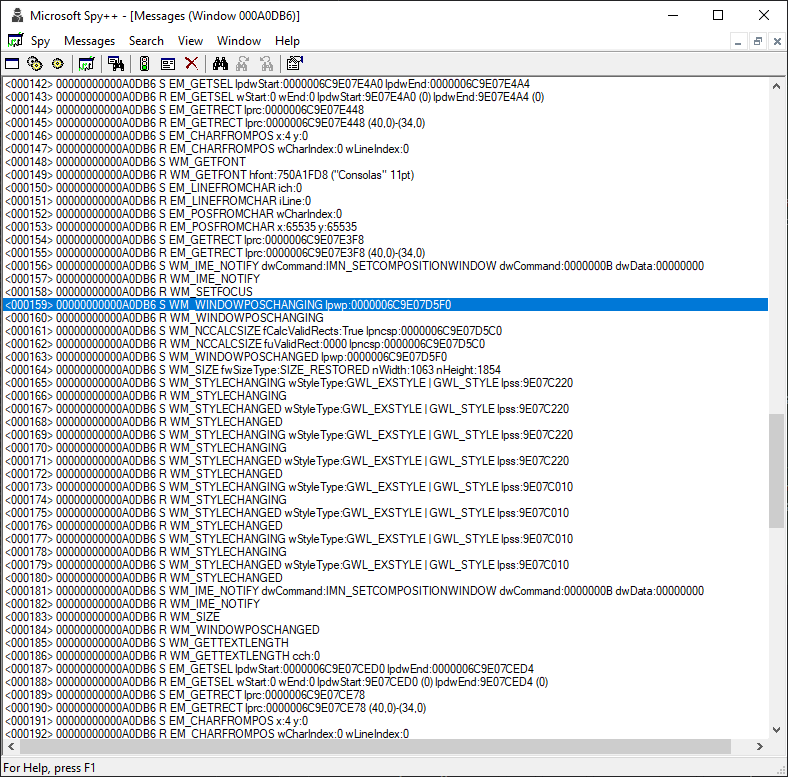
Using Microsoft Spy++, we see the following:
Ok, great! It looks like the WM_WINDOWPOSCHANGING event gets fired, so we can hook that event. Searching the Fancy Zones code base for WM_WINDOWPOSCHANGING yields... nothing.
Hitting up Google, yields this interesting hit:
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17436795/setwineventhook-window-maximized-event
void CALLBACK exampleHook(HWINEVENTHOOK hook, DWORD event, HWND hWnd, LONG idObject, LONG idChild, DWORD dwEventThread, DWORD dwmsEventTime) { if (EVENT_OBJECT_LOCATIONCHANGE == event) { WINDOWPLACEMENT wp; wp.length = sizeof(WINDOWPLACEMENT); GetWindowPlacement(hWnd, &wp); if (SW_SHOWMAXIMIZED == wp.showCmd) { // Window is maximized. } } }
Ok, so this guy says to hook the EVENT_OBJECT_LOCATIONCHANGE event, let's search, which results in a few hits, all in FancyZonesApp.cpp: - One - Another
Step 1: Update FancyZonesApp.cpp¶
First, update FancyZonesApp.cpp so that we're always listening to EVENT_OBJECT_LOCATIONCHANGE events.
std::array<DWORD, 7> events_to_subscribe = {
EVENT_SYSTEM_MOVESIZESTART,
EVENT_SYSTEM_MOVESIZEEND,
EVENT_OBJECT_NAMECHANGE,
EVENT_OBJECT_UNCLOAKED,
EVENT_OBJECT_SHOW,
EVENT_OBJECT_CREATE,
EVENT_OBJECT_LOCATIONCHANGE
};
Step 2: Update FancyZones.cpp¶
else if (message == WM_PRIV_LOCATIONCHANGE)
{
// If the window is being resized via handle bars
if (m_draggingState.IsDragging())
{
if (auto monitor = MonitorFromPoint(ptScreen, MONITOR_DEFAULTTONULL))
{
MoveSizeUpdate(monitor, ptScreen);
}
}
else
{
auto hwnd = reinterpret_cast<HWND>(wparam);
if (FancyZonesWindowUtils::IsWindowMaximized(hwnd))
{
auto monitor = MonitorFromWindow(hwnd, MONITOR_DEFAULTTONULL);
MoveToAppLastZone(hwnd, monitor, NULL);
}
}
}
Example 2: Parent Windows¶
Example 3: DLL-Injection¶
There are two ways to inject DLLs: - SetWindowsHookEx() - CreateRemoteThread()
SetWindowsHookEx¶
Considerations¶
- Global vs per-Thread
- Hook type: WH_GETMESSAGE, WH_CALLWNDPROC, ...
- 32-bit / 64-bit processes
- Windows Store Apps
Debugging Tips¶
CreateRemoteThread¶
DLL Injection References¶
- https://www.apriorit.com/dev-blog/679-windows-dll-injection-for-api-hooks
- https://isaratech.com/cpp-dll-injection-using-createremotethread-on-windows/
- https://www.vicarius.io/blog/wtf-is-frida/
- https://github.com/rsmudge/vncdll/tree/master/rdll
References¶
- https://github.com/Taloth/PowerToys/commit/80ddcd08b9fa9537a4d5148735fe2fc9273aecb8
- https://github.com/microsoft/PowerToys/wiki/Fancy-Zones-deep-dive
- https://devblogs.microsoft.com/oldnewthing/20210104-00/?p=104656
-
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1295999/event-when-a-window-gets-maximized-un-maximized
-
https://forums.codeguru.com/showthread.php?364445-How-to-detect-if-window-is-maximizing
Things I Considered¶
- Making application window a child of a parent window
- DirectComposition